Summary
Discreet Log Contracts (DLCs) are a smart contract structure designed to address scalability, data integration, and privacy issues. DLCs involve two parties creating a multisig address and choosing an oracle, which publishes commitments to messages for data settlement. The contract is settled using encrypted adapter signatures that can only be decrypted with information from the signed oracle message. A timelocked refund transaction ensures that both parties are refunded if the oracle fails to broadcast the necessary information. However, DLCs face challenges with network scalability and potential free option issues. LN Markets has proposed a new DLC specification to address the needs of institutional actors. Their proposal introduces a DLC coordinator to facilitate contract negotiations and prevent free options. The coordinator holds the funding transaction signatures and is incentivized to submit the transaction. The proposal also includes liquidation options and the ability to add additional margin. These modifications make DLCs more suitable for institutional investors and financial markets. This advancement has the potential to greatly impact Bitcoin’s use in capital markets.
Key Points
1. Discreet Log Contracts (DLCs) were proposed by Thaddeus Dryja in 2017 to address scalability, data integration, and privacy issues in smart contract schemes. DLCs use a multisig address and an oracle to create Contract Execution Transactions (CETs) that interact with the oracle to settle the contract based on external data. DLCs provide scalability, allow external data to be brought into the blockchain, and ensure privacy for users.
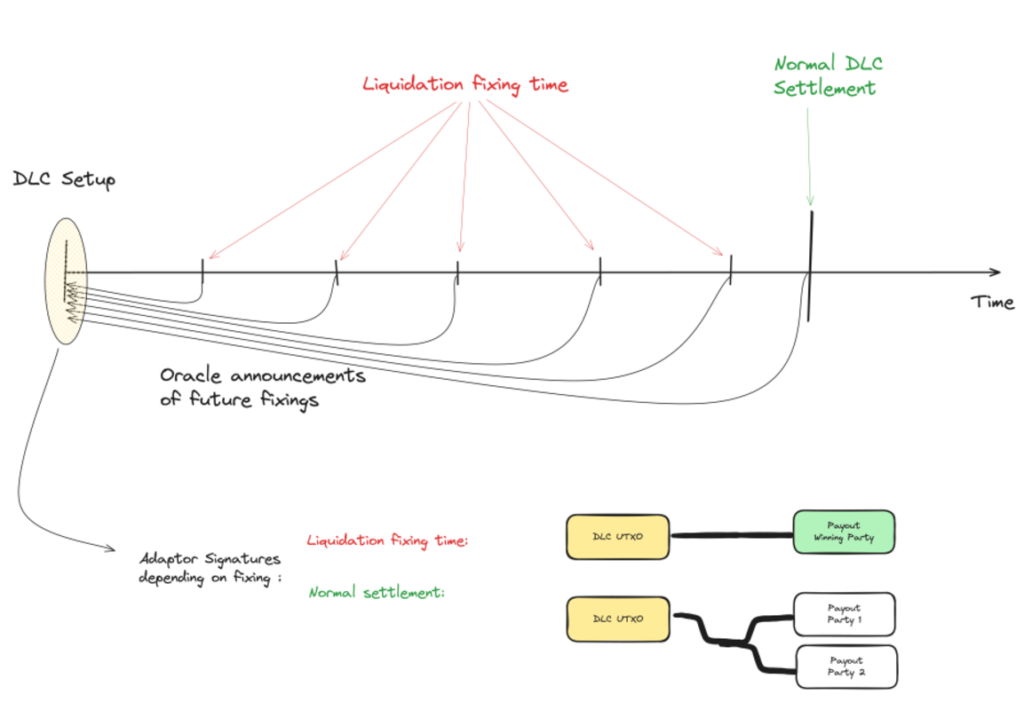
2. LN Markets has introduced a new DLC specification tailored towards institutional actors. This specification addresses issues such as the free options problem, lack of margin calls, and inefficient capital usage. The introduction of a DLC coordinator facilitates contract negotiations, prevents free options, and improves the coordination process of constructing the DLC. The coordinator also enables reliable communication for liquidations and adding additional margin.
3. The involvement of a coordinator in DLCs allows for efficient management of liquidity, early contract settlement based on market conditions, and the ability to add more collateral in response to upcoming liquidation events. These capabilities make DLCs more attractive to institutional investors and expand their potential use in capital and financial markets. This development is seen as a significant advancement for the use of Bitcoin in these industries.