Summary
TLDR: The blockchain is a decentralized mechanism that timestamps digital information without a central operator, providing cryptographic guarantees. Bitcoin’s value lies in its commitment to information using private/public key cryptography, merkle trees, and hash algorithms. Blockspace is priced in bytes, making dense information, like economic value transfers, competitive. Merkle trees can timestamp an infinite amount of data outside of Bitcoin transactions, offering potential for timestamping more than just money. Opentimestamps and Mainstay provide scalable solutions for timestamping data, while para-consensus systems can extend Bitcoin’s commitments. Bitcoin is more than just money, serving as a decentralized timestamping system mapping digital data in space and time.
Key Points
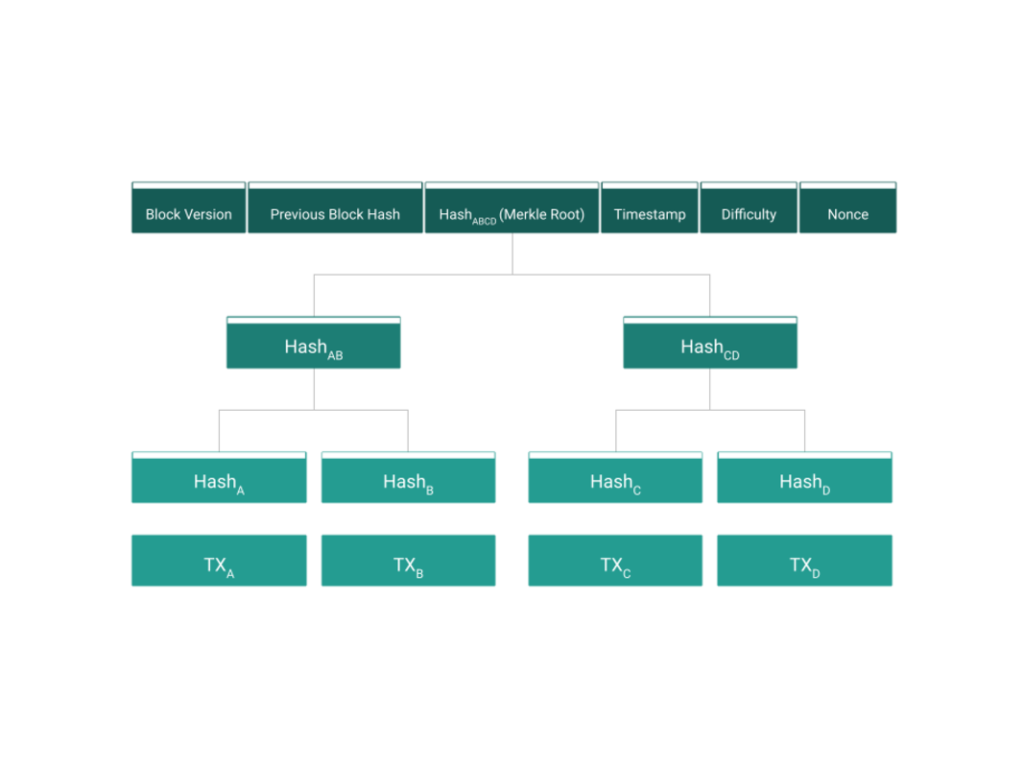
1. The blockchain technology relies on private/public key cryptography, merkle trees, and hash algorithms to provide cryptographic guarantees around the order of digital information, enabling decentralized mechanisms with no centralized authority.
2. The use of blockspace in Bitcoin transactions is priced in bytes, giving denser information a competitive advantage in getting included in a block. The transfer of economic value remains the primary use case of Bitcoin due to its density in information.
3. Merkle trees in the Bitcoin blockchain have no size limit, allowing for the commitment of infinite amounts of data outside of Bitcoin transactions themselves. This enables the blockchain to be used as a timestamping tool for a wide range of applications beyond just monetary transactions.